Multi-Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud: What’s the Difference and Which is Right for You in 2024?
In the dynamic field of information technology, cloud computing has cemented itself as a fundamental component for businesses and organizations worldwide. As we navigate through 2024, understanding the various cloud computing models becomes crucial for IT professionals. This article aims to demystify two prominent cloud strategies: multi-cloud and hybrid cloud. While both approaches offer unique benefits, distinguishing between them is key to leveraging their full potential. This educational material will dissect the differences, advantages, and use cases of each model, assisting IT professionals in making informed decisions about which strategy aligns best with their organizational goals.
Defining Cloud Computing Models
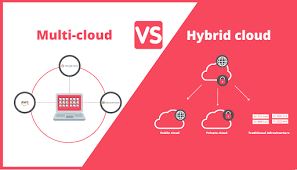
Multi-Cloud
A multi-cloud strategy involves using cloud services from multiple providers. This model allows organizations to distribute their resources across various cloud environments, be it public, private, or a combination. Key characteristics of a multi-cloud setup include:
- Provider Diversity: By utilizing services from different cloud providers, organizations can optimize performance and cost.
- Customization: It allows for a more tailored approach, as specific needs can be met by specific providers.
- Risk Management: Diversifying providers can reduce dependence on a single vendor, mitigating risks related to downtime or vendor lock-in.
Hybrid Cloud
In contrast, a hybrid cloud strategy combines private cloud or on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services. This model is characterized by:
- Integration: It seamlessly blends private and public cloud infrastructures, allowing data and applications to move between them.
- Security and Compliance: By keeping sensitive data on-premises or in a private cloud, hybrid models can offer enhanced security and compliance.
- Flexibility: It provides the best of both worlds – the scalability of public clouds and the security of private clouds.
Contrast with Single-Cloud Models
Unlike single-cloud models that rely on one provider for all cloud services, multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud strategies offer greater flexibility and risk management. The choice between a single cloud and these more complex setups depends on specific organizational needs and goals.
Evolution of Cloud Strategies
The landscape of cloud computing has undergone significant transformations since its inception. Initially, organizations gravitated towards single-cloud models due to their simplicity and straightforward management. However, as the complexity of business needs and technological advancements grew, the shift towards multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies became evident.
From Single to Multi-Cloud
The transition to multi-cloud environments was primarily driven by the desire for greater flexibility and the need to avoid vendor lock-in. As cloud technologies evolved, businesses realized that relying on a single provider could lead to limitations in terms of capabilities and cost efficiencies. Multi-cloud strategies emerged as a solution, offering a mix of services from various providers that could cater to specific organizational needs, ranging from data analytics to customer relationship management.
Emergence of Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud models emerged from the need to balance the flexibility of cloud computing with the control and security of on-premises infrastructure. This approach became particularly appealing for industries with stringent data privacy regulations or for businesses that required high levels of data security. The hybrid cloud model allowed for sensitive data to be kept on private servers while still leveraging the scalability and efficiency of public cloud services for less critical operations.
Technological Drivers
Key technological advancements have facilitated this evolution. The development of more sophisticated cloud management tools, improved integration capabilities, and advancements in data security have all played pivotal roles. These technologies have made it more feasible for organizations to manage complex cloud environments effectively.
The evolution from single-cloud to multi-cloud and hybrid cloud models reflects the changing needs and capabilities of organizations in the digital age. The next sections will delve deeper into the advantages of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud environments.
Advantages of Multi-Cloud Environments (300 words)
Multi-cloud environments offer a range of benefits that cater to diverse business needs and technological demands.
Flexibility and Choice in Cloud Services
The foremost advantage of a multi-cloud approach is the flexibility it offers. Organizations can select the best services from various providers based on performance, features, and cost. For instance, one provider might offer superior data analytics services, while another might excel in customer relationship management. This choice empowers organizations to tailor their cloud infrastructure to their specific needs.
Risk Mitigation through Diversification
By spreading resources across multiple cloud providers, organizations can mitigate risks related to provider outages or data loss. This diversification ensures that the failure of one provider doesn’t bring the entire operation to a halt. It also addresses concerns of vendor lock-in, providing businesses with the leverage to negotiate better terms and conditions.
Cost Optimization Strategies
A multi-cloud strategy enables cost optimization. Different providers offer varying pricing models, and organizations can utilize the most cost-effective options for different services. For example, one cloud provider might offer more affordable storage options, while another might have better pricing for computing power.
Enhanced Customization and Scalability
Multi-cloud environments allow organizations to customize their IT infrastructure extensively. They can scale up or down based on demand, optimizing resource usage and performance. This scalability is particularly beneficial for businesses with fluctuating demands.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud Environments
Hybrid cloud environments blend the capabilities of private and public clouds, offering unique advantages, especially in terms of security, compliance, and operational flexibility.
Integrated Approach Combining On-Premises and Cloud Resources
The hybrid model provides an integrated solution that combines the security and control of on-premises infrastructure with the scalability and efficiency of the cloud. This integrated approach is ideal for companies that handle sensitive data or operate in regulated industries, as it allows for critical data to be stored in a private cloud or on-premises while still utilizing the public cloud for less sensitive operations.
Enhanced Security and Compliance Controls
One of the primary benefits of a hybrid cloud is the enhanced security it provides. Sensitive data can be kept on private servers, which are often subject to stricter security measures than public clouds. Additionally, this model aids in meeting compliance requirements, as sensitive data can be processed and stored according to specific regulatory standards.
Operational Flexibility
Hybrid clouds offer operational flexibility, allowing businesses to leverage the public cloud for high-demand periods or specific tasks while maintaining core systems on their private cloud or on-premises. This flexibility ensures that businesses can adapt to changes in demand without compromising on performance or security.
Case Scenarios Where Hybrid Cloud is Advantageous
Hybrid clouds are particularly advantageous in sectors like healthcare, finance, and government, where data privacy is paramount. They also benefit organizations looking to gradually transition to the cloud, allowing them to maintain existing infrastructure while leveraging cloud technologies.
Choosing Between Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud
When determining whether a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy is more suitable, organizations must consider various factors, each aligning with distinct business needs and operational contexts.
Key Factors to Consider
- Organization Size and Complexity: Larger organizations with complex needs may benefit more from a multi-cloud strategy due to its flexibility and scalability. In contrast, smaller to mid-sized businesses might find a hybrid cloud more manageable and cost-effective.
- Data Security Needs: For businesses handling sensitive data, such as those in healthcare or finance, the hybrid cloud offers enhanced security features. The ability to store critical data in a private environment while still enjoying the scalability of public clouds is a significant advantage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations under strict regulatory mandates may lean towards hybrid cloud solutions. The control over data location and processing in a hybrid setup helps in adhering to compliance requirements.
- Budget Constraints: Budget is a critical factor. Multi-cloud environments might require more significant investment in management and integration tools, whereas hybrid clouds can be a more budget-friendly option, especially for organizations already possessing substantial on-premises infrastructure.
- Industry-Specific Considerations: Certain industries have unique requirements that might make one model more appealing than the other. For instance, industries requiring high data throughput and processing capabilities might favor multi-cloud for its performance optimization options.
Future Scalability and Adaptability
An organization’s future growth trajectory should also influence the choice. A model that suits the current needs but is scalable and adaptable for future expansion and technological advancements is crucial.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, both multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies come with their set of challenges.
- Technical Complexities: Managing multiple cloud environments or integrating on-premises infrastructure with cloud services can be technically complex. It requires skilled personnel and robust management tools.
- Management and Monitoring Challenges: Keeping track of various services, especially in a multi-cloud scenario, can be daunting. Effective monitoring and management are essential to ensure smooth operations and cost-effectiveness.
- Security Concerns: While both models offer security advantages, they also introduce unique security challenges. Ensuring consistent security policies across multiple clouds or between cloud and on-premises environments is critical.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud models depends on an organization’s specific needs, size, industry, and future growth plans. While multi-cloud offers unparalleled flexibility and optimization, hybrid cloud provides a balanced mix of security and scalability. The decision should align with business objectives, operational capabilities, and long-term strategic goals. As cloud computing continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable is essential for IT professionals navigating these choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the primary difference between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies?
- A1: The primary difference lies in their structure. Multi-cloud involves using cloud services from multiple cloud providers, whereas hybrid cloud combines private cloud or on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services.
Q2: Who should consider using a multi-cloud strategy?
- A2: Organizations seeking flexibility, wanting to avoid vendor lock-in, and looking to optimize costs and performance across various cloud services should consider a multi-cloud strategy. It is particularly beneficial for large organizations with complex and diverse needs.
Q3: What are the main advantages of a hybrid cloud model?
- A3: Hybrid cloud models offer enhanced security and control, as they allow sensitive data to be kept on-premises or in a private cloud. They also provide the scalability of public clouds and are particularly suitable for businesses with strict regulatory compliance requirements.
Q4: Is a multi-cloud environment more expensive than a hybrid cloud?
- A4: The cost can vary based on the specific needs and usage patterns of an organization. Multi-cloud environments might require more investment in integration and management, whereas hybrid clouds can be more cost-effective for those with existing on-premises infrastructure.
Q5: How do security concerns differ between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud setups?
- A5: In multi-cloud setups, security concerns revolve around managing disparate security policies and potential vulnerabilities across multiple platforms. In hybrid clouds, the challenge is to maintain consistent security measures between on-premises/private cloud and public cloud environments.
Q6: Can small businesses benefit from multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategies?
- A6: Yes, small businesses can benefit from both strategies, depending on their specific needs. A hybrid cloud can be ideal for those with limited budgets but needing enhanced security, while a multi-cloud approach can offer scalability and flexibility as the business grows.
Q7: What should be considered when transitioning to a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud model?
- A7: Organizations should consider factors like their specific business needs, budget, existing IT infrastructure, technical expertise, security requirements, and compliance needs. A thorough assessment of these factors will guide the decision-making process.
Q8: How does regulatory compliance impact the choice between multi-cloud and hybrid cloud?
- A8: Regulatory compliance often requires strict data management and security protocols. A hybrid cloud model is generally preferred for its ability to keep sensitive data in a more controlled environment, making it easier to comply with such regulations.
Q9: Are there specific industries that prefer one model over the other?
- A9: Yes. For instance, industries like healthcare and finance, which handle sensitive data, may prefer hybrid clouds for security reasons. Industries focusing on digital innovation and customer experience might lean towards multi-cloud for its flexibility and optimization capabilities.
Q10: How does an organization’s size influence its choice of cloud model?
- A10: Larger organizations with diverse and complex needs might find more value in a multi-cloud model due to its scalability and flexibility. Smaller organizations or those with less complexity might prefer the hybrid cloud for its cost-effectiveness and security advantages.